Creating a resume builder with React, NodeJS and AI 🚀
In this article, you'll learn how to create a resume builder using React, Node.js, and the OpenAI API. What's better to look for a job and say you have build a job resume builder with AI to do so? 🤩

A small request 🥺
I produce content weekly, and your support helps so much to create more content. Please support me by clicking the “Love” button. You probably want to “Save” this article also, so you can just click both buttons. Thank you very very much! ❤️
Introduction to the OpenAI API
GPT-3 is a type of artificial intelligence program developed by OpenAI that is really good at understanding and processing human language. It has been trained on a huge amount of text data from the internet, which allows it to generate high-quality responses to a wide range of language-related tasks.
For this article we will use OpenAI GPT3.Once the ChatGPT API is out, I will create another article using it 🤗I have been a big fan of OpenAI from the day they released their first API, I have turned to one of the employees and sent them a nice request to get access to the beta version of GPT3, and I got it 😅

That’s me in Dec 30, 2020, Begging for access.
Novu – the first open-source notification infrastructure
Just a quick background about us. Novu provides a unified API that makes it simple to send notifications through multiple channels, including In-App, Push, Email, SMS, and Chat. With Novu, you can create custom workflows and define conditions for each channel, ensuring that your notifications are delivered in the most effective way possible.

I would be super happy if you could give us a star! And let me also know in the comments ❤️ https://github.com/novuhq/novu
Project Setup
Here, I’ll guide you through creating the project environment for the web application. We’ll use React.js for the front end and Node.js for the backend server.
Create the project folder for the web application by running the code below:
Setting up the Node.js server
Navigate into the server folder and create a package.json file.
Install Express, Nodemon, and the CORS library
ExpressJS is a fast, minimalist framework that provides several features for building web applications in Node.js, CORS is a Node.js package that allows communication between different domains, and Nodemon is a Node.js tool that automatically restarts the server after detecting file changes.
Create an index.js file – the entry point to the web server.
Set up a Node.js server using Express.js. The code snippet below returns a JSON object when you visit the http://localhost:4000/api in your browser.
Configure Nodemon by adding the start command to the list of scripts in the package.json file. The code snippet below starts the server using Nodemon.
Congratulations! You can now start the server by using the command below.
Setting up the React application
Navigate into the client folder via your terminal and create a new React.js project.
Install Axios and React Router. React Router is a JavaScript library that enables us to navigate between pages in a React application. Axios is a promise-based Node.js HTTP client for performing asynchronous requests.
Delete the redundant files, such as the logo and the test files from the React app, and update the App.js file to display Hello World as below.
Navigate into the src/index.css file and copy the code below. It contains all the CSS required for styling this project.
Building the application user interface
Here, we’ll create the user interface for the resume builder application to enable users to submit their information and print the AI-generated resume.
Create a components folder within the client/src folder containing the Home.js, Loading.js, Resume.js, ErrorPage.js files.
From the code snippet above:
- The
Home.jsfile renders the form field to enable users to enter the necessary information. - The
Loading.jscontains the component shown to the user when the request is pending. - The
Resume.jsdisplays the AI-generated resume to the user. - The
ErrorPage.jsis shown when an error occurs.
Update the App.js file to render the components using React Router.
The Home page
Here, you’ll learn how to build a form layout that can send images via HTTP request and dynamically add and remove input fields.
First, update the Loading component to render the code snippet below, shown to the user when the resume is pending.
Next, update the ErrorPage.js file to display the component below when users navigate directly to the resume page.
Copy the code snippet below into the Home.js file
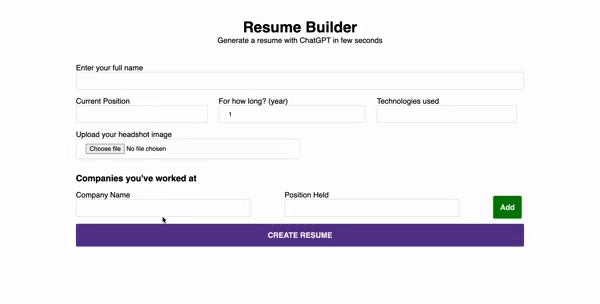
The code snippet renders the form field below. It accepts the full name and current work experience – (year, position, title) and allows the user to upload a headshot image via the form field.
Lastly, you need to accept the user’s previous work experience. So, add a new state that holds the array of job descriptions.
Add the following functions which help with updating the state.
The handleAddCompany updates the companyInfo state with the user’s input, handleRemoveCompany is used to remove an item from the list of data provided, and the handleUpdateCompany updates the item properties – (name and position) within the list.
Next, render the UI elements for the work experience section.
The code snippet maps through the elements within the companyInfo array and displays them on the webpage. The handleUpdateCompany function runs when a user updates the input field, then handleRemoveCompany removes an item from the list of elements, and the handleAddCompany adds a new input field.
The Resume page
This page shows the resume generated from the OpenAI API in a printable format. Copy the code below into the Resume.js file. We’ll update its content later in this tutorial.
How to submit images via forms in Node.js
Here, I’ll guide you on how to submit the form data to the Node.js server. Since the form contains images, we’ll need to set up Multer on the Node.js server.
💡 Multer is a Node.js middleware used for uploading files to the server.
Setting up Multer
Run the code below to install Multer
Ensure the form on the frontend application has the method and encType attributes, because Multer only process forms which are multpart.
Import the Multer and the Node.js path packages into the index.js file
Copy the code below into the index.js to configure Multer.
- From the code snippet above:
- The
app.use()function enables Node.js to serve the contents of anuploadsfolder. The contents refer to static files such as images, CSS, and JavaScript files. - The
storagevariable containingmulter.diskStoragegives us full control of storing the images. The function above stores the images in the upload folder and renames the image to its upload time (to prevent filename conflicts). - The upload variable passes the configuration to Multer and set a size limit of 5MB for the images.
- The
Create the uploads folder on the server. This is where the images will be saved.
How to upload images to a Node.js server
Add a route that accepts all the form inputs from the React app. The upload.single("headshotImage") function adds the image uploaded via the form to the uploads folder.
Update the handleFormSubmit function within the Home.js component to submit the form data to the Node.js server.
The code snippet above creates a key/value pair representing the form fields and their values which are sent via Axios to the API endpoint on the server. If there is a response, it logs the response and redirect the user to the Resume page.
How to communicate with the OpenAI API in Node.js
In this section, you’ll learn how to communicate with the OpenAI API within the Node.js server.We’ll send the user’s information to the API to generate a profile summary, job description, and achievements or related activities completed at the previous organisations. To accomplish this:
Install the OpenAI API Node.js library by running the code below.
Log in or create an OpenAI account here.
Click Personal on the navigation bar and select View API keys from the menu bar to create a new secret key.
Copy the API Key somewhere safe on your computer; we’ll use it shortly.
Configure the API by copying the code below into the index.js file.
Create a function that accepts a text (prompt) as a parameter and returns an AI-generated result.
The code snippet above uses the text-davinci-003 model to generate an appropriate answer to the prompt. The other key values helps us generate the specific type of response we need.
Update the /resume/create route as done below.
The code snippet above accepts the form data from the client, converts the workHistory to its original data structure (array), and puts them all into an object.
Next, create the prompts you want to pass into the GPTFunction.
- From the code snippet above:
- The
remainderTextfunction loops through the array of work history and returns a string data type of all work experiences. - Then, there are three prompts with instructions on what is needed from the GPT-3 API.
- Next, you store the results in an object and log them to the console.
- The
Lastly, return the AI-generated result and the information the users entered. You can also create an array representing the database that stores results as done below.
Displaying the response from the OpenAI API
In this section, I’ll guide you through displaying the results generated from the OpenAI API in a readable and printable format on a web page.
Create a React state within the App.js file. The state will hold the results sent from the Node.js server.
From the code snippet above, only setResult is passed as a prop into the Home component and only result for the Resume component. setResult updates the value of the result once the form is submitted and the request is successful, while result contains the response retrieved from the server, shown within the Resume component.
Update the result state within the Home component after the form is submitted and the request is successful.
Update the Resume component as done below to preview the result within the React app.
The code snippet above displays the result on the webpage according to the specified layout. The function replaceWithBr replaces every new line (\n) with a break tag, and the handlePrint function will enable users to print the resume.
How to print React pages using the React-to-print package
Here, you’ll learn how to add a print button to the web page that enables users to print the resume via the React-to-print package.
💡 React-to-print is a simple JavaScript package that enables you to print the content of a React component without tampering with the component CSS styles.
Run the code below to install the package
Import the library within the Resume.js file and add the useRef hook.
Update the Resume.js file as done below.
The handlePrint function prints the elements within the componentRef – main tag, sets the document’s name to the user’s full name, and runs the alert function when a user prints the form.
Congratulations! You’ve completed the project for this tutorial.
Here is a sample of the result gotten from the project:

Conclusion
So far, you’ve learnt:
- what OpenAI GPT-3 is,
- how to upload images via forms in a Node.js and React.js application,
- how to interact with the OpenAI GPT-3 API, and
- how to print React web pages via the React-to-print library.
This tutorial walks you through an example of an application you can build using the OpenAI API. With the API, you can create powerful applications useful in various fields, such as translators, Q&A, code explanation or generation, etc.
The source code for this tutorial is available here:
https://github.com/novuhq/blog/tree/main/resume-builder-with-react-chatgpt-nodejs
Thank you for reading!
Help me out!
If you feel like this article helped you, I would be super happy if you could give us a star! And let me also know in the comments ❤️
https://github.com/novuhq/novu



